Kinematics links - Every part of machine which have relative motion to another part. → The link should be resistance body. What is resistant body? →Under the action of force it can transfer motion and power. Kinematics links →1. Rigid links 2. Flexible links 3. Fluid links Rigid links - There is no deformation. Ex - piston,connecting rod Flexible links - Deformation is allowed under permissible limits. Ex - Belt drive Fluid links - A fluid link is one that is deformed by having fluid in a closed vessel and the motion is transmitted through the fluid by pressure. Ex - Hydraulic press Types of links - 1. Singular 2. Binary 3. Ternary 4. Quaternary links
I.C engine - two stroke cycle - four stroke cycle - difference between two stroke four stroke - auto ignition -carburetion - scavenging -supercharging
I.C ENGINE
Difference of petrol and diesel engine :-
1.Petrol engine run on otto cycle and diesel engine run on diesel cycle.
2.Air fuel mixture suction Stroke in petrol engine.In diesel engine only air sucks in suction stroke.
3.In petrol engine,spark plug is needed.In diesel engine,no spark plug is needed.
4.In petrol engine,compression ratio 6-12.
In diesel engine,compression ratio 14-22.
5.In petrol engine,high efficiency.
In diesel engine low efficiency.
6.In petrol engine,less vibration & noise.
In diesel engine,more vibration & noise.
7.Petrol engine light weight engine.
Diesel engine heavy weight engine.
8.Petrol engine generaly use motor cycle,car,light weight vehicles.
Diesel engine generaly use truck,bus etc.
GOVERNINNG OF I.C ENGINES : Various methods are : a. Heat and miss governing — used for small engine,No fuel admited during the cycle by keeping suction valve closed.
b. Quantitative governing — Quantity of charge varried.
c. Qualitative governing — Quality of charge is valid.
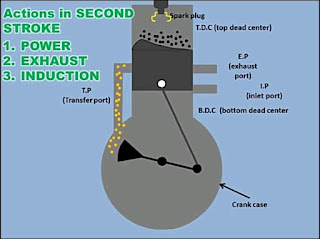
TWO STROKE CYCLE ENGINE :
Difference of petrol and diesel engine :-
1.Petrol engine run on otto cycle and diesel engine run on diesel cycle.
2.Air fuel mixture suction Stroke in petrol engine.In diesel engine only air sucks in suction stroke.
3.In petrol engine,spark plug is needed.In diesel engine,no spark plug is needed.
4.In petrol engine,compression ratio 6-12.
In diesel engine,compression ratio 14-22.
5.In petrol engine,high efficiency.
In diesel engine low efficiency.
6.In petrol engine,less vibration & noise.
In diesel engine,more vibration & noise.
7.Petrol engine light weight engine.
Diesel engine heavy weight engine.
8.Petrol engine generaly use motor cycle,car,light weight vehicles.
Diesel engine generaly use truck,bus etc.
GOVERNINNG OF I.C ENGINES : Various methods are : a. Heat and miss governing — used for small engine,No fuel admited during the cycle by keeping suction valve closed.
b. Quantitative governing — Quantity of charge varried.
c. Qualitative governing — Quality of charge is valid.
TWO STROKE CYCLE ENGINE :
In two stroke engines,the two ideal i.e, suction and exhaust stroke are not eligible,(in other word suction & exhaust stroke are not separate stroke).so,we have one power stroke revolution of crank in two stroke engines.
In two stroke engine,ports are use instead of inlet & exhaust valve,its operated by complicated mechanisms.The charge is collected in the oil casing which is compressed during power stroke.sunce,it is at high pressure,therefore it automatically enters the cylinder ports are cleared off the piston.
FOUR STROKE CYCLE ENGINE :-
In four stroke engine have four separate stroke(suction,compression,power,exhaust),two separate revolution of crankshaft & during thermo dynamic cycle.
*Auto-ignition: It is the phenomenon of fuel catching fire without external source of ignition energy.
*Carburetion : Is the process braking up the petrol into fine partical & mixing air it with air in desired proportion.
*Supercharging : is the process of supplying greater mass of air to engine cylinder by compressing intake air initially view to obtain high power.it is essentially at high altitudes where density of atmospheric air is low.
*Scavenging : It's the process to remove the burn gagses from engine cylinder.
Comments
Post a Comment